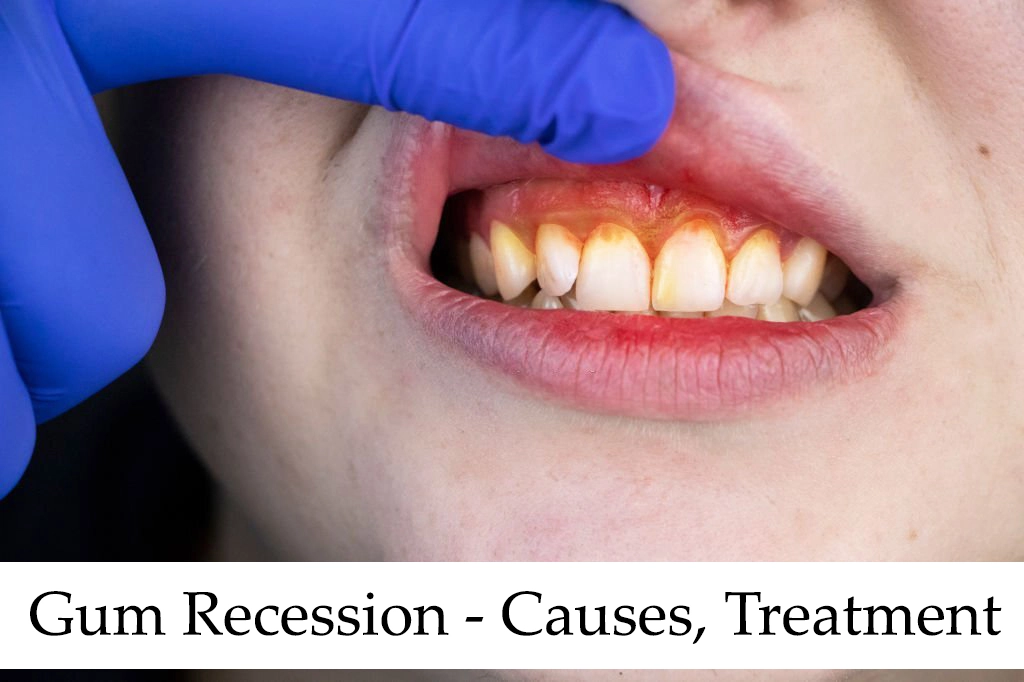
No matter how many social media platforms pop up, a beautiful smile is still the best way to connect with people. Yet, your smile’s beauty can be marred by dental issues like crooked teeth, tooth loss, and receding gums. Gum recession is a dental condition in which your gum tissue starts shrinking away from your teeth, exposing their roots.
If left unchecked, receding gums can create pockets between the teeth and gum line. The pockets soon become infected with bacteria that compromise the underlying bone structure, leading to tooth loss. Now, that’s something to chew on.
As gum recession is not a matter to be taken lightly, we’ll help you learn more about it, including identifying early signs and what you can do to prevent gum disease below.
Learn More About Gum Recession
Gum recession is a form of periodontal (gum) disease caused by harsh or irregular brushing and poor oral hygiene.
You need healthy gum tissue to surround and protect your teeth. Once the tissue becomes infected and wears down, it pulls back, exposing your teeth’s roots.
Receding gums lead to cavities and increased sensitivity while brushing and eating. Tooth loss caused by shrinking gums can further affect your smile and mental well-being. The inability to chew your food properly can also result in nutritional deficiency.
It’s hard to notice gum recession in its early stages. Most patients visit the dentist when the tissue withdrawal becomes obvious, i.e., during the moderate or severe stages. Depending on how long you’ve had it, gum or gingival recession can affect a single tooth or spread to multiple teeth.
Regular dental check-ups can help catch gum disease early on. You can book a dental check-up with the experienced dentists at Osseo Family Dental in Osseo, MN.
Who Does It Affect? How Common is it?
Gum recession occurs in people of all ages. However, those above the age of 65 are at a higher risk of developing gum infection and disease.
Experts estimate that nearly 50% of Americans over the age of 32 have some form of gum or periodontal disease.
Gum Recession: Causes and Symptoms
While the leading cause of gum recession is poor oral health, here are some other factors that can contribute to it:
- brushing too roughly or aggressively
- plaque or tartar buildup
- misalignment or abnormal tooth positioning
- injury or trauma to gum tissue
- teeth misalignment
- smoking or chewing tobacco
- tongue or lip piercings
- periodontal disease
- genetic predisposition to thin/receding gums
- diabetes and old age
Whatever may be the cause of your receding gum line, you need to keep a watch for the following symptoms to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment:
- swollen, red, or tender gums
- bleeding while brushing/flossing
- pus or discharge from gums
- development of pockets between your teeth
- bad breath
- difficulty chewing
- sharp sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods
- your teeth appear to be visibly longer
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, you should see your family dentist right away.
How is Gum Recession Diagnosed?
Once you have booked a session with your family dentist, you should tell them about your symptoms. Your dentist will then perform a routine examination and diagnose gum recession using a periodontal probe to measure the tissue loss on each tooth.
They may also check the size of the pockets between your teeth. Pockets measuring 5 millimeters or more are a sure sign of gum disease or recession.
Can Gum Recession Be Stopped? How is it Treated?
You can stop gum recession by getting proper treatment and practicing better oral health care. Unfortunately, you cannot grow back the lost tissue, but you can prevent the situation from worsening.
Treatment for gum recession involves treating the infection to prevent further degeneration of gum tissue and preserve the exposed tooth roots. Therefore, You may need to consult a periodontist, a dentist specializing in gum disease for the more severe cases.
The treatments for receding gums fall into 2 main categories, non-surgical and surgical.
Non-surgical treatments include:
- Scaling and Root Planing: The first order of business while treating receding gums is to remove the plaque, hardened tartar, and bacteria-infested tissue from your gums. A deep dental cleaning (scaling and root planing) is performed under local anesthesia to remove the infection. In case of severe gum infection, your periodontist may inject antibiotics directly under the gums to stop further spread.
- Dental Bonding: The tooth roots bared by gum recession are at a higher risk of developing cavities. They do not have an enamel coating, as they are supposed to be protected by gum tissue.
Dental bonding covers these uncovered roots with a tooth-colored resin that protects your tooth and decreases sensitivity. The resin coating also helps your teeth look normal and feel more comfortable while chewing.
Your periodontist may also ask you to use the following:
- Topical antibiotic gel
- Antibacterial or antimicrobial mouthwash
- Antiseptic chips
- Enzyme suppressants
Now, a surgical approach can involve any of the following treatments:
- Flap Surgery: If non-surgical measures fail to control gum recession, your dentist can perform open flap scaling and planing. However, The infected gum tissue is pulled back to clean the bacteria and tartar buildup inside the gums. Once the roots are clean, the gum tissue is put back in place for a snug fit.
- Regeneration: The bacteria and plaque are removed from above and below the gum line under this technique. Next, a regenerative material, like a graft tissue, membrane, or tissue-stimulating protein, is applied to restore the damaged bone and tissue naturally.
- Gum Grafts: In severe gum recession, the dentist may recommend gum graft surgery. The procedure involves taking tissue from healthy gums or your mouth’s roof area and grafting it to the receding gum line to cover the exposed tooth roots.
Post-surgery, you will get a detailed list of post-operative care instructions. You need to follow these diligently for a speedy and complete recovery.
Once you have recovered, you will need to be extra vigilant about your oral hygiene to prevent further gum infection and recession.
How to Prevent Gum Recession?
Follow the pointers shared below to enjoy good oral health and prevent gum disease or recession from recurring:
- Firstly, Use a soft-bristled brush to clean your teeth at least twice daily.
- Secondly, Floss once a day.
- After that, Use an antimicrobial mouthwash after brushing, especially at night.
- Schedule regular teeth cleanings with your dentists. Moreover, You can get once every 6 months or more frequently if your dentist thinks you need it.
- Avoid smoking or chewing tobacco.
We will now answer a few commonly-asked questions on gum recession.
FAQs
- Can gum recession be reversed?
Ans. Unfortunately, gum tissue does not regenerate like other tissues. So, you cannot grow back your gums. Proper treatment and oral care can prevent further tissue loss.
- How much does gum recession treatment cost?
Ans. The cost of gum recession treatment depends upon the severity of the gum disease and whether you need surgical or non-surgical treatment. The best way is to schedule an appointment with a specialist and get an estimate.
- How do I reduce the sensitivity caused by gum recession?
Ans. You can reduce tooth sensitivity by using a soft-bristled brush and fluoride toothpaste. Avoid brushing your teeth too harshly and see your dentist immediately in case of any bleeding or inflamed gums.
Worried About Your Shrinking Gum Line? Schedule an Appointment at Osseo Family Dental Now!
Contact Osseo Family Dental today if you are looking for a team of dental experts who can successfully diagnose and treat gum diseases, including gum recession!
You can call us at: (763) 425 – 2626 or email us at: info@osseofamilydental.com.